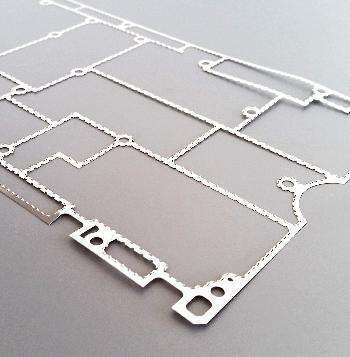
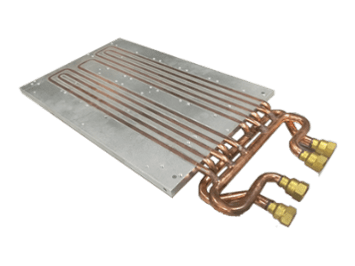
Engineering and Manufacturing of components for
EMI shielding & Thermal Dissipation.
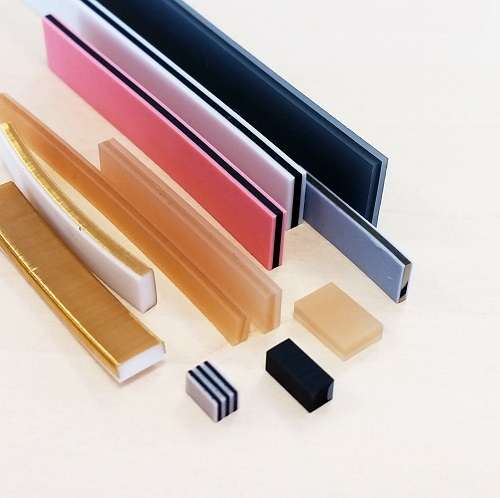
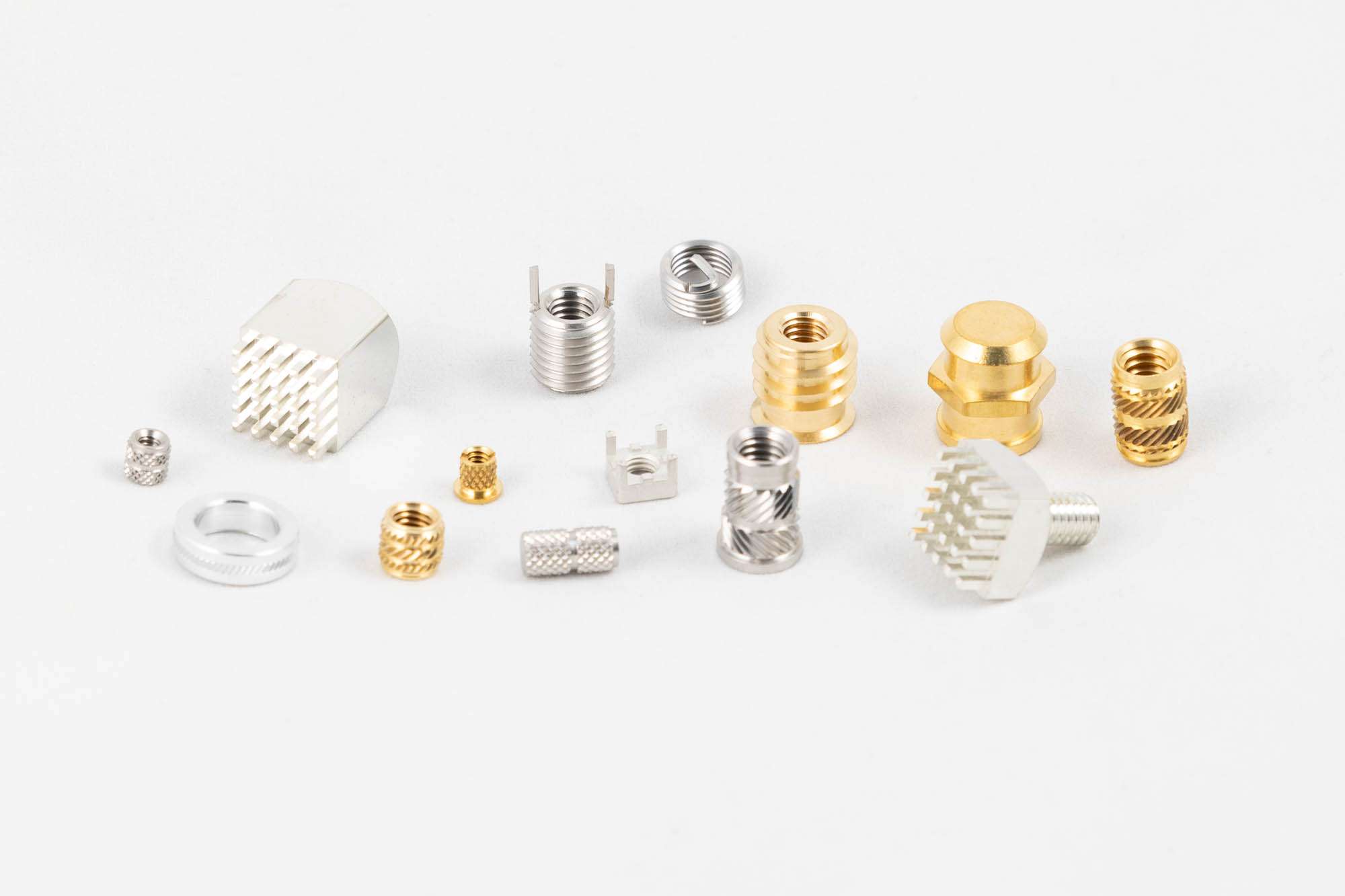
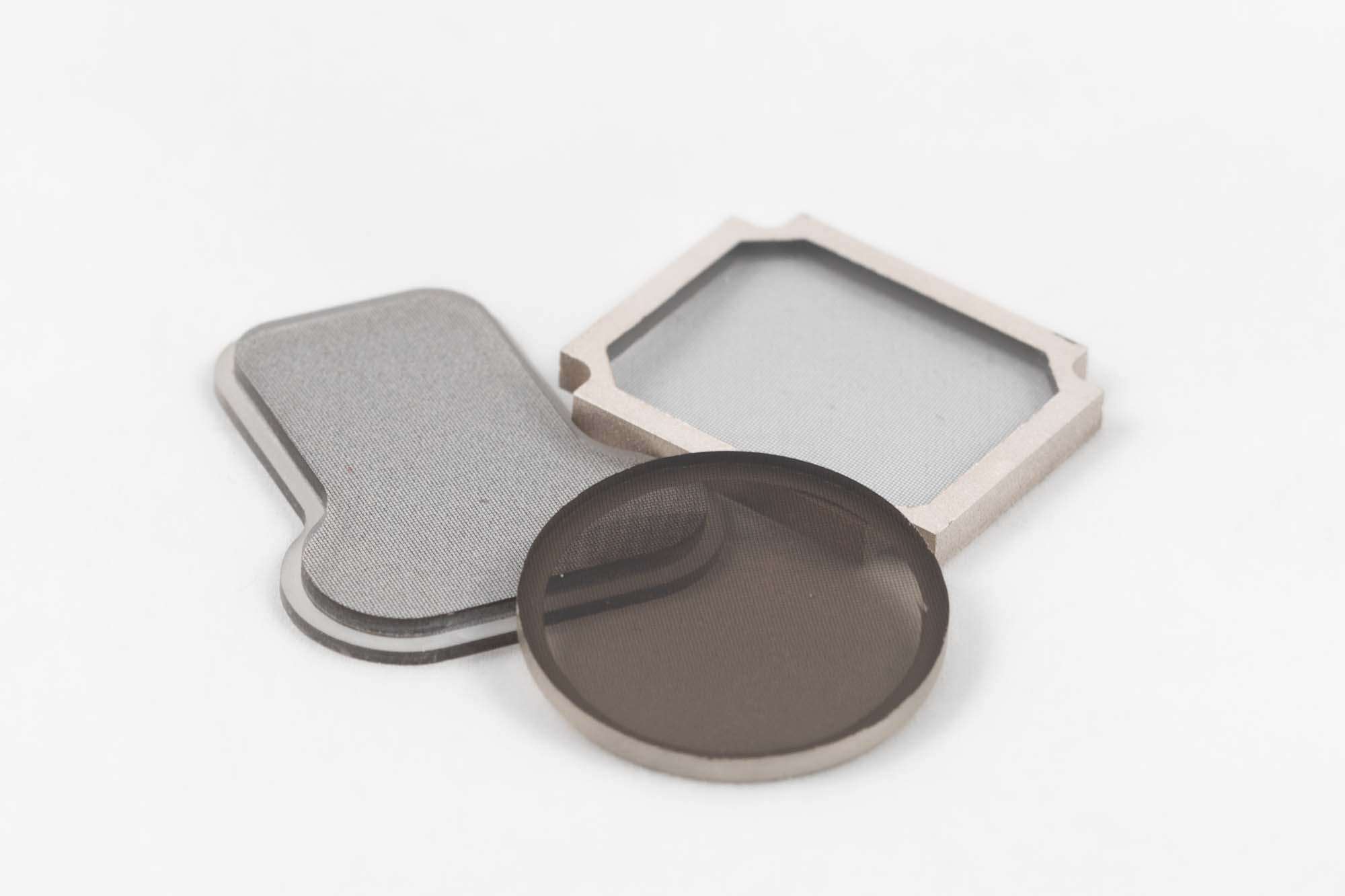
Compelma supplies passive components for EMI shielding and thermal dissipation. Our EMI and Thermal products are standards and customs, from prototyping to mass production. We supply to the main industrial actors worldwide.
Discover Integrated Products by COMPELMA




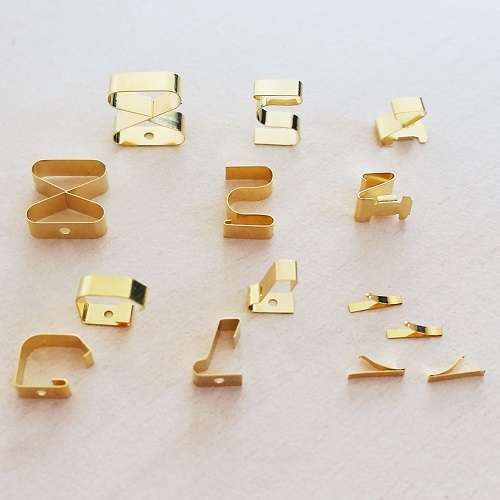
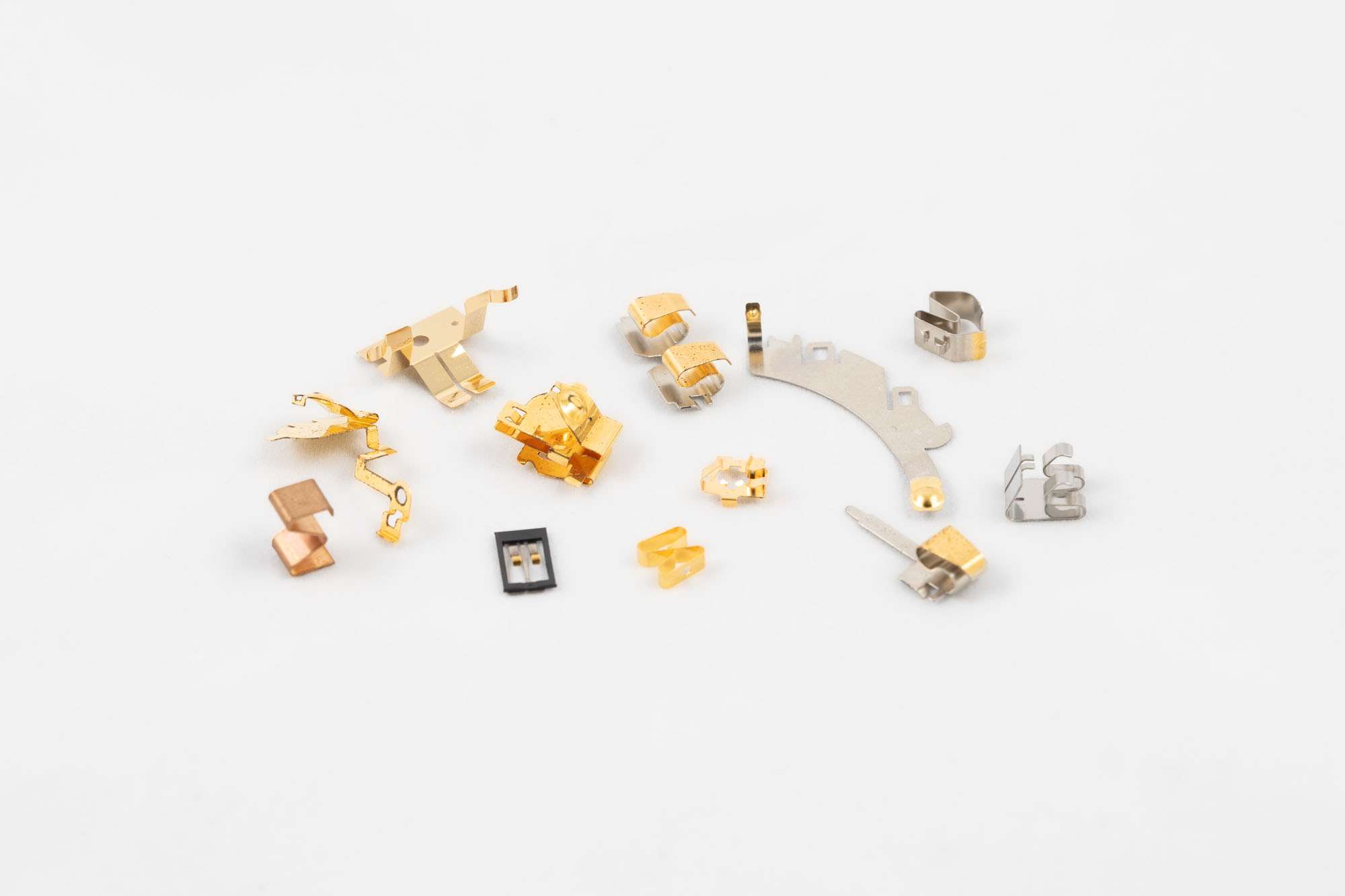
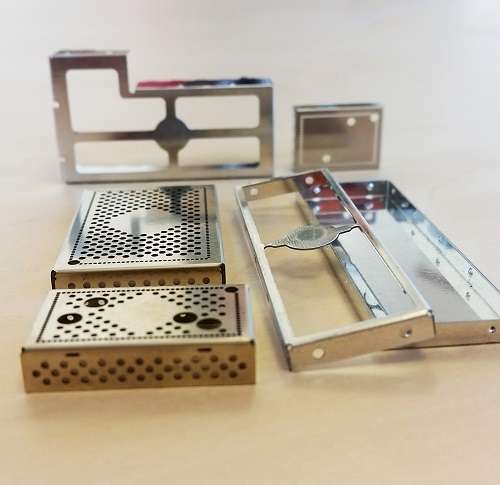
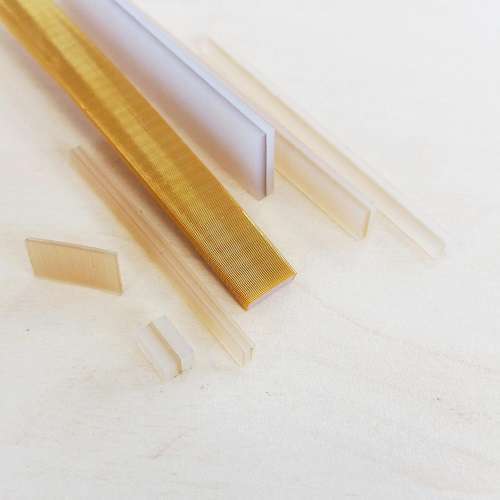
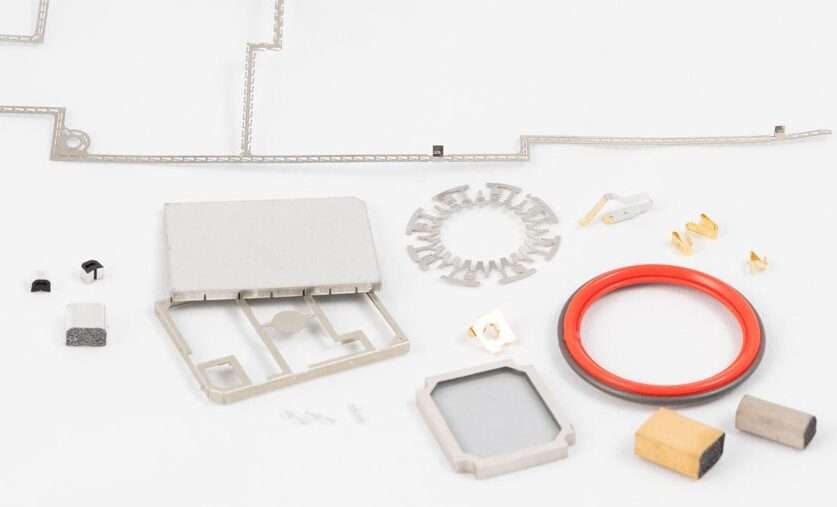
We provide all passive components to solve and mastering EMI (Electromagnetic Compatibility) on all of your projects.
Each of our EMI component and technology can be customised for a seamless integration on your project.
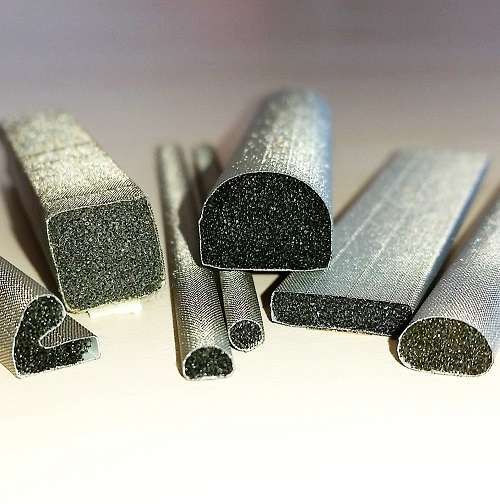
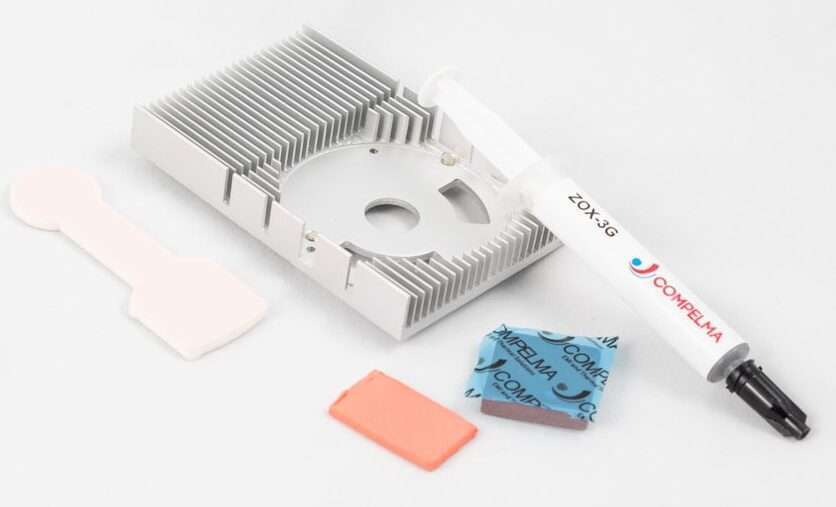
All our components to master thermal dissipation on your electronic projects.
Each of these technologies for thermal dissipation can be declined to perfectly reach your specifications and requirements.
We provide EMI shielding and thermal dissipation on multiple sectors

Industry

Automotive

Medical

Military

Telecommunication
They trust us for EMI shielding and thermal dissipation

Compelma is a main actor in providing standard and custom passive components for EMI and Thermal dissipation for electronic projects.
We are working with the biggest industrial actors since more than 30 years. We are nowadays providing parts in more than 27 countries over the world.
With 90% of our solutions tailor-made and the highest norms accreditation we are fully involved in providing the most efficient, reliable and cost efficient products for your projects.
Our main value are reactivity, Innovation and Partnership. They are integrated on all of our projects and guarantee a high quality prestation.

International Network
Our longterm partnerships with suppliers and carriers all over the world are a main asset to deliver quickly the best parts for your projects.
60% of our turnover is done on French Market.
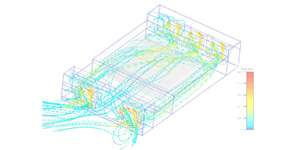
Tools and simulation
Our tooling is adapted to make parts from prototyping to mass production.
Our expertise is an asset to provide the most efficient solution based on our experience.
Over 80% of our products are tailor made.

Groupe ICE
Member of the ICE Groupe since 2006, a federation of 20 industrial companies working together.
ICE Groupe gather 1 150 employees and is making over 175M€ of turnover.
Our International Partner Network
Become Our Local Representative
We are seeking dedicated representatives to join us in delivering cutting-edge Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) and thermal management solutions across the globe.
With substantial market potential and lucrative opportunities within the B2B sector, there has never been a better time to partner with us.
Your collaboration is highly valued, and once we establish our partnership, we will ensure you receive exclusive benefits such as competitive margins and personalized support tailored to your needs.
We invite you to become an exclusive representative in your country, where you will enjoy regional protection, priority order processing, and dedicated shipping services.
If you are a business operating in related fields and seeking innovative products to enhance your portfolio, we encourage you to explore our solutions. Reach out to us, and we will help you find the perfect offerings for your clients.
Let’s work together to achieve success and develop our companies!
COMPELMA
COMPELMA
1 Rue Terre Neuve
91940 Les Ulis – FRANCE
https://compelma.com
IMPO RF
IMPO RF :
124 Mohaliver St.
Yehud, IL, 56209
Po Box 7016
ISRAEL
https://www.imporf.com/
TIRANGA AEROSPACE
TIRANGA AEROSPACE
#501, 4th Floor,
G.G. Complex,
Vidyaranyapura,
Bengaluru – 560097
INDIA
https://www.tirangaaerospace.com/index.html
CCC SOLUTIONS
CCC SOLUTIONS
Smedkalles väg 15,
184 38 Åkersberga, SWEDEN
https://cccsolutions.eu/
RENAUDIN
RENAUDIN
Kavacık Mahallesi
Okul Caddesi
Güngör Plaza
No:21 Kat:6
Beykoz / ISTANBUL
TÜRKİYE
https://www.renaudin.com.tr/fr/emi-emc-rf-fr/
EP ELECTRONIC PRINT
EP ELECTRONIC PRINT
Am Weidegrund 8 & 10,
82194 Gröbenzell – GERMANY
www.ep-electronicprint.de